Step-by-step Example
Setting up a coupled conjugate heat transfer problem can broadly be boiled down to the following steps:
Create an OpenFOAM case.
Including an OpenFOAM mesh.
Write a MOOSE input file to run that case.
You'll need to specify the coupled boundaries and the time step.
Write a MOOSE input file to solve the MOOSE part of the problem and include the previous MOOSE input file as a Multiapp.
Use the Multiapp system to set boundary conditions and couple the parts of the solve.
In this example we'll run through how to set up the 'Flow Over Heated Plate' example defined on PreCICE's website. We'll use OpenFOAM to solve the heat transfer problem in the fluid domain and use MOOSE's heat conduction module to solve the solid domain.
We're going to use the 'heat flux forward' method to solve the conjugate heat transfer problem: we transfer the heat flux the same way as the heat is flowing. As the solid domain is hot in this example, we will transfer the heat flux from the MOOSE solve and set it as a Neumann boundary condition on the OpenFOAM case. We will transfer the wall temperature from OpenFOAM and set that as a Dirichlet boundary condition on the MOOSE solve. These transfers will occur at every time step.
Fluid and solid domains.
Setting Up the OpenFOAM Case
Generally, when setting up an OpenFOAM case, you start by looking for similar examples in your OpenFOAM installation's tutorials folder and tweaking the settings. In this case, however, PreCICE has already defined an OpenFOAM case for this problem. Download the fluid-openfoam folder from the precice/tutorials GitHub repository.
The OpenFOAM mesh is defined in fluid-openfoam/system/blockMeshDict. To generate the mesh, run blockMesh on the fluid-openfoam folder:
$ blockMesh -case fluid-openfoam
To decompose the mesh for parallel execution, use OpenFOAM's decomposePar tool.
$ decomposePar -case fluid-openfoam
The case is set up to use 2 processors. You can change this within the fluid-openfoam/system/decomposeParDict file.
For more info on the OpenFOAM case structure, see the OpenFOAM docs.
Write a MOOSE Input File for the OpenFOAM Case
Problem
First, we define the Problem block, which tells Hippo we are running an OpenFOAM case and provides the functionality to couple OpenFOAM into the MOOSE framework.
# fluid.i
[Problem]
type = FoamProblem
[]
Mesh
The first block to define is the mesh block. Hippo provides the FoamMesh class to read an OpenFOAM mesh and generate a MOOSE mesh along given boundaries.
In this example, the boundary we're interested in coupling to the MOOSE solve is called 'interface'.
# fluid.i
[Mesh]
type = FoamMesh
case = 'fluid-openfoam' # the directory of the OpenFOAM case
foam_patch = 'interface' # the name of the coupled boundary
[]
You can use the --mesh-only option to have a look at the boundary mesh Hippo generates for you.
$ hippo-opt -i fluid.i --mesh-only
$ paraview fluid_in.e
Transferring data from OpenFOAM to MOOSE
To access OpenFOAM variables from MOOSE, Hippo provides the FoamVariable system, which allows you to shadow OpenFOAM volume fields and function objects with MOOSE variables, which are automatically updated after each OpenFOAM solve. For this problem, the fluid temperature is required by MOOSE. In OpenFOAM, the temperature is stored in the volScalarField named T:
# fluid.i
[FoamVariables]
[fluid_wall_temp]
type = FoamVariableField
foam_variable = T
[]
[]
Internally, Hippo creates AuxVariables which can use MOOSE's transfer system and so can be transferred between MOOSE apps.
Imposing boundary conditions on OpenFOAM from MOOSE
Hippo also implements the FoamBC system that allows you to impose boundary conditions on OpenFOAM from the Hippo input file. In this case, we wish to impose a heat flux BC on the temperature field. This requires the FoamFixedGradientBC, which mirrors OpenFOAM's fixedGradient BC type. As in this case, we provide a heat flux, we must also provide the thermal conductivity, which is specified as the diffusivity_coefficient. kappa is the name of the thermal conductivity variable in OpenFOAM.
# fluid.i
[FoamBCs]
[solid_heat_flux]
type = FoamFixedGradientBC
foam_variable = T
diffusivity_coefficient = kappa
[]
[]
Similar to FoamVariable, this creates an AuxVariable with name solid_heat_flux under the hood. MOOSE's transfers system can be used to set the values in the AuxVariable, that are then imposed on the OpenFOAM solver's boundary.
Executioner
Set the time step settings in the Executioner block. Hippo provides the FoamTimeStepper class to set the time step configuration of the OpenFOAM solve. These settings will override any time step settings in the OpenFOAM case's controlDict.
# fluid.i
[Executioner]
type = Transient
start_time = 0
end_time = 10
dt = 0.025
[TimeStepper]
type = FoamTimeStepper
[]
[]
You can now run the OpenFOAM case using hippo-opt -i fluid.i! Although, the result won't be very interesting as we haven't set up the solid domain of the problem yet.
Write a MOOSE Input File for the Solid Domain
Mesh
Let's generate a mesh for the solid domain. In the OpenFOAM case, the mesh is graded in the x direction (the elements are smaller for smaller x coordinates). To avoid unnecessary interpolations in our solve, let's make sure our meshes conform along their shared boundary, by setting bias_x.
# flow_over_heated_plate.i
[Mesh]
[solid]
type = GeneratedMeshGenerator
boundary_name_prefix = solid
dim = 3
nx = 161
xmin = 0
xmax = 1
ny = 16
ymin = -0.25
ymax = 0
nz = 1
zmin = 0
zmax = 0.4
# Calculated here:
# https://openfoamwiki.net/index.php/Scripts/blockMesh_grading_calculation
# Based on a grading factor of 5 and 161 elements.
bias_x = 1.010109749
[]
[]
Heat Conduction Problem
Let's set up the MOOSE heat conduction problem for the solid domain. The bottom of the heated plate is held at 310 K.
# flow_over_heated_plate.i
[Variables]
[temp]
family = LAGRANGE
order = FIRST
initial_condition = 310
[]
[]
[Kernels]
[heat-conduction]
type = HeatConduction
variable = temp
[]
[heat-conduction-dt]
type = HeatConductionTimeDerivative
variable = temp
[]
[]
[BCs]
[fixed_temp]
type = DirichletBC
variable = temp
boundary = solid_bottom
value = 310
[]
[]
[Materials]
# The example specifies that the thermal diffusivity of the solid should
# be α = 1 m2/s, and the thermal conductivity should be k = 100 W/(m.K).
#
# We know α = k/(ρ.Cp), where k is thermal conductivity, Cp is specific
# heat capacity, and ρ is density.
#
# Hence we require that ρ.Cp = k = 100.
[thermal-conduction]
type = HeatConductionMaterial
thermal_conductivity = 100.0 # W/(m.K)
specific_heat = 0.5 # J/(kg.K)
[]
[thermal-density]
type = GenericConstantMaterial
prop_names = 'density'
prop_values = 200.0 # kg/m3
[]
[]
[Executioner]
type = Transient
start_time = 0
end_time = 10
dt = 0.025
fixed_point_abs_tol = 1e-7
fixed_point_rel_tol = 1e-8
solve_type = 'PJFNK'
petsc_options = '-snes_ksp_ew'
petsc_options_iname = '-pc_type -pc_hypre_type'
petsc_options_value = 'hypre boomeramg'
nl_abs_tol = 1e-7
nl_rel_tol = 1e-8
[]
[Outputs]
exodus = true
[]
This problem is now runnable, although is not very interesting either - the temperature simply sits at 310 K.
Computing Heat Flux
For us to transfer the boundary heat flux from the solid to fluid domain, we must first calculate it. Hippo provides the HeatFluxAux auxiliary kernel for this purpose.
# flow_over_heated_plate.i
[AuxVariables]
[wall_heat_flux]
family = MONOMIAL
order = CONSTANT
initial_condition = 0
[]
[]
[AuxKernels]
[heat_flux_aux]
type = HeatFluxAux
variable = wall_heat_flux
thermal_conductivity = 100 # W/(m.K)
T = temp
boundary = 'solid_top'
[]
[]
Coupling the Solves
To couple the solves we're going to:
include the
fluid.iinput file as a multiapp.transfer OpenFOAM's wall temperature and set it as a BC on the solid solve.
transfer the boundary heat flux in the solid to the multiapp and set it as a BC on the fluid solve.
# flow_over_heated_plate.i
[MultiApps]
[hippo]
type = TransientMultiApp
app_type = hippoApp
execute_on = timestep_begin
input_files = 'fluid.i'
[]
[]
[AuxVariables]
...
# Add an AuxVariable to store the wall temperature of the fluid domain.
[fluid_wall_temperature]
family = LAGRANGE
order = FIRST
initial_condition = 0
[]
[]
[Transfers]
# Copy the wall temperature from the fluid into an AuxVariable.
# This was stored in the FoamVariable fluid_wall_temp
[wall_temperature_from_fluid]
type = MultiAppGeometricInterpolationTransfer
source_variable = fluid_wall_temp
from_multi_app = hippo
variable = fluid_wall_temperature
execute_on = same_as_multiapp
[]
# Copy the heat flux from the 'wall_heat_flux' aux variable into the
# 'solid_heat_flux' FoamBC in the multiapp.
[heat_flux_to_fluid]
type = MultiAppGeometricInterpolationTransfer
source_variable = wall_heat_flux
to_multi_app = hippo
variable = solid_heat_flux
execute_on = same_as_multiapp
[]
[]
[BCs]
...
# Use the fluid wall temperature as a matched value boundary condition.
[fluid_interface]
type = MatchedValueBC
variable = temp
boundary = solid_top
v = fluid_wall_temperature
[]
[]
We're done!
For simplicity, we're using the same time step settings in both input files. However, you could enable sub cycling in the multiapp block if you require shorter time steps for one of the domains.
Run the problem in serial using
$ hippo-opt -i flow_over_heated_plate.i
or in parallel (remembering to reconstruct the OpenFOAM case for your post-processing):
$ mpirun -n 2 hippo-opt -i flow_over_heated_plate.i && reconstructPar -case fluid-openfoam
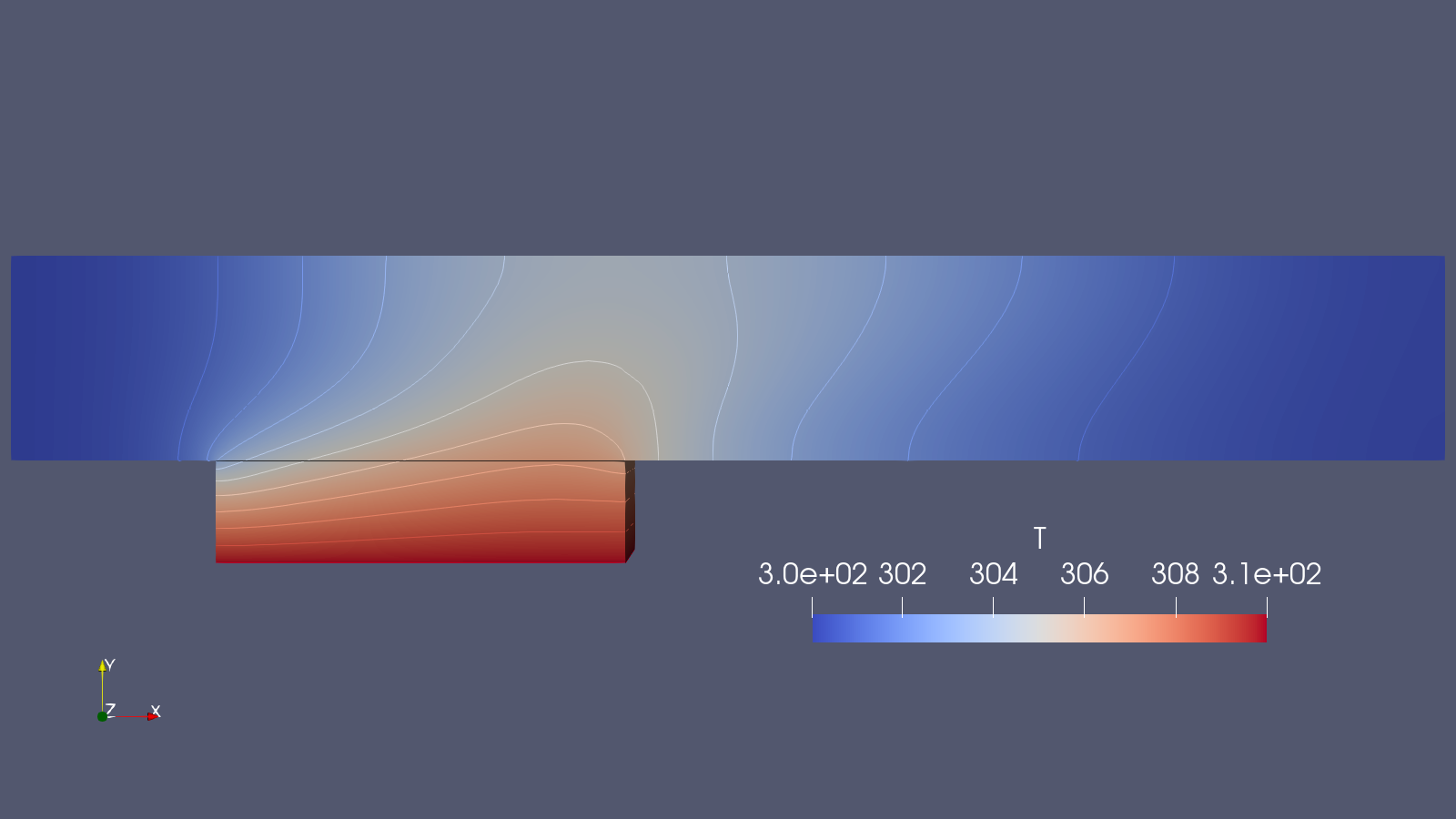
The result of the coupled solve after 10 seconds.
Find the completed input files below:
[Mesh]
type = FoamMesh
case = 'fluid-openfoam' # the directory of the OpenFOAM case
foam_patch = 'interface' # the name of the coupled boundary
[]
[FoamVariables]
[fluid_wall_temp]
type = FoamVariableField
foam_variable = 'T'
initial_condition = 300
[]
[]
[FoamBCs]
[solid_heat_flux]
type = FoamFixedGradientBC
foam_variable = 'T'
diffusivity_coefficient = kappa
initial_condition = 0
[]
[]
[Problem]
type = FoamProblem
[]
[Executioner]
type = Transient
start_time = 0
end_time = 10
dt = 0.025
[TimeStepper]
type = FoamTimeStepper
[]
[]
[Mesh]
[solid]
type = GeneratedMeshGenerator
boundary_name_prefix = solid
dim = 3
nx = 161
xmin = 0
xmax = 1
ny = 16
ymin = -0.25
ymax = 0
nz = 1
zmin = 0
zmax = 0.4
# Calculated here:
# https://openfoamwiki.net/index.php/Scripts/blockMesh_grading_calculation
# Based on a grading factor of 5 and 161 elements.
bias_x = 1.010109749
[]
[]
[Variables]
[temp]
family = LAGRANGE
order = FIRST
initial_condition = 310
[]
[]
[Kernels]
[heat-conduction]
type = HeatConduction
variable = temp
[]
[heat-conduction-dt]
type = HeatConductionTimeDerivative
variable = temp
[]
[]
[BCs]
[fixed_temp]
type = DirichletBC
variable = temp
boundary = solid_bottom
value = 310
[]
# Use the fluid wall temperature as a matched value boundary condition.
[fluid_interface]
type = MatchedValueBC
variable = temp
boundary = solid_top
v = fluid_wall_temperature
[]
[]
[Materials]
# The example specifies that the thermal diffusivity of the solid should
# be α = 1 m2/s, and the thermal conductivity should be k = 100 W/(m.K).
#
# We know α = k/(ρ.Cp), where k is thermal conductivity, Cp is specific
# heat capacity, and ρ is density.
#
# Hence we require that ρ.Cp = k = 100.
[thermal-conduction]
type = HeatConductionMaterial
thermal_conductivity = 100.0 # W/(m.K)
specific_heat = 0.5 # J/(kg.K)
[]
[thermal-density]
type = GenericConstantMaterial
prop_names = 'density'
prop_values = 200.0 # kg/m3
[]
[]
[AuxVariables]
[wall_heat_flux]
family = MONOMIAL
order = CONSTANT
initial_condition = 0
[]
# Add an AuxVariable to store the wall temperature of the fluid domain.
[fluid_wall_temperature]
family = LAGRANGE
order = FIRST
initial_condition = 0
[]
[]
[AuxKernels]
[heat_flux_aux]
type = HeatFluxAux
variable = wall_heat_flux
thermal_conductivity = 100 # W/(m.K)
T = temp
boundary = 'solid_top'
[]
[]
[MultiApps]
[hippo]
type = TransientMultiApp
app_type = hippoApp
execute_on = timestep_begin
input_files = 'fluid.i'
[]
[]
[Transfers]
# Copy the wall temperature from the fluid into an AuxVariable.
[wall_temperature_from_fluid]
type = MultiAppGeometricInterpolationTransfer
source_variable = fluid_wall_temp
from_multi_app = hippo
variable = fluid_wall_temperature
execute_on = same_as_multiapp
[]
# Copy the heat flux from the 'wall_heat_flux' aux variable into the
# multiapp.
# Remember we marked the 'solid_heat_flux' variable in 'fluid.i' to be
# used as a heat flux boundary condition on the OpenFOAM solve.
[heat_flux_to_fluid]
type = MultiAppGeometricInterpolationTransfer
source_variable = wall_heat_flux
to_multi_app = hippo
variable = solid_heat_flux
execute_on = same_as_multiapp
[]
[]
[Executioner]
type = Transient
start_time = 0
end_time = 10
dt = 0.025
fixed_point_abs_tol = 1e-7
fixed_point_rel_tol = 1e-8
solve_type = 'PJFNK'
petsc_options = '-snes_ksp_ew'
petsc_options_iname = '-pc_type -pc_hypre_type'
petsc_options_value = 'hypre boomeramg'
nl_abs_tol = 1e-7
nl_rel_tol = 1e-8
[]
[Outputs]
exodus = true
[]